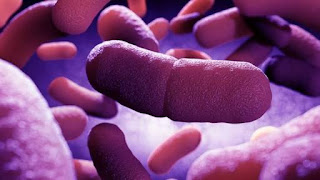
Yersinia pestis, this plague germs are rod-shaped stocky, with rounded ends. The size is approximately 1.5 x 5.7 microns and coloration are Gram-negative. Germs show pleomorphism properties with an assortment of shapes With staining, visible under the microscope bacteria form bipolar (two poles) that is similar to the pin. Germs do not move, do not form spores and is always covered with slime.
In cultured in medium aerobic or facultative anaerobes, bacteria optimum growth at a temperature of 27 ° C with an optimum pH of 7.2.
Transmission of plague, plague often cause epidemics in many countries, even the plague pandemic that strikes people in dozens of countries around the world, leaving a death toll of millions of lives. Actual bubonic plague is an infectious disease in mice cities (Rattus norvegicus) and mice (Rattus rattus) is the infection spread to humans through the bite of the rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis and Ceratophyllus fasciatus). In addition plague germs can be transmitted through the air (droplet infection) come and people with pneumonic plague.
Clinical symptoms of Plague
Plague in humans can occur in two forms, namely the shape and form of pulmonary plague bubo plague.
Bubonic plague, After passing through an incubation period of between 2-8 days, groin lymph nodes to swell followed by formation of pus. Patients suffering from fever and cough. If the bacteria enter the bloodstream it will happen septikemi accompanied by bleeding skin and mucous membranes. Sometimes it happens that severe neurological disorder that causes sufferers died.
Pneumonic plague. It also called bubonic plague pneumonia that occurs through the respiratory air transmission causing clinical symptoms such as cough, fever and symptoms of pneumonia accompanied by cough blood. Patients often experience severe cyanosis due to respiratory distress suffered.
Germs can be isolated and Yersinia pestis blood, sputum and pus patients were then examined under a microscope to determine the exact diagnosis of disease plague. To help with the diagnosis do serology plague, for example agglutination test, ELISA, complement fixation test, and immunofluorescent antibody (IFA).
Treatment of plague, In the early stages, patients can be treated with streptomycin, tetracycline or kioramfenikol, with satisfactory results. Without treatment, patients with plague pneumonia will generally die
prevention of Plague, Because it is so contagious, plague sufferers should be isolated and treated immediately. People who had contact with the patient must also be quarantined and closely monitored and given preventive treatment with tetrasikiin or sulfonamides. Everyone who will visit the plague endemic areas should be vaccinated to prevent contracting the disease plague.
Prevention of zoonotic diseases should be accompanied by eradication of rodents and rodent using rodenticides, while the rat fleas eradicated by insecticides.

0 Comment
Markup